Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the C while loop statement to execute a code block repeatedly based on a condition.
Introduction C while loop statement #
The C while loop statement allows you to execute a code block repeatedly based on a condition checked at the beginning of each iteration.
Here’s the syntax of the while loop statement:
while (expression)
{
statement;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)How it works:
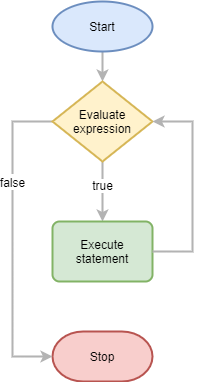
The while statement first evaluates the expression. If the result is non-zero (true), the while statement executes the statement within its body. This cycle continues until the expression becomes zero (or false).
The while statement re-checks the expression at the beginning of each iteration before executing the statement. Therefore, at some point, the expression needs to become zero (or false) to end the loop. Otherwise, you’ll have an indefinite loop.
When the while statment is first encountered and the expression is zero (or false), the while statement won’t execute the statement at all. The program passes the control to the statement that follows the while statement.
The following flowchart illustrates how while loop works:
C while loop examples #
Let’s take some examples of using the while loop statement
1) Simple C while loop statement #
The following example uses the while loop statement to display five numbers from 0 to 4:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while (n < 5)
{
printf("%d ", n);
n++;
}
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Output:
0 1 2 3 4Code language: plaintext (plaintext)How it works.
- First, declare the
nvariable and initialize it to0. - Second, check if
nis less than5before entering the loop. - Third, display
nand add 1 to it in each iteration. Repeat this cycle untilnis not less than5.
Since n starts with zero, the while statement executes 5 iterations.
2) Using the C while loop to develop a number-guessing game #
The following example illustrates how to use the while loop statement to create the number guessing game:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
// maximum number of guesss
const int MAX_GUESS = 4;
int secret_number, // secret number
number = -1, // input number
guess = 0; // number of guesses
// Get a random number between 0 and 10
srand(time(NULL)); // call once only
secret_number = rand() % 10 + 1;
while (number != secret_number && guess < MAX_GUESS)
{
// increase the guess
guess++;
// prompt for an input
printf("\nPlease enter a number (0 - 10):");
scanf("%d", &number);
// check the input against the secret number
if (number == secret_number)
{
printf("Bingo! you got it.\n");
}
else
{
if (number > secret_number)
printf("No, it is smaller.\n");
else
printf("No, it is bigger.\n");
// show the remaining guesses
if (MAX_GUESS - guess > 0)
printf("%d guess(es) left\n", MAX_GUESS - guess);
else
printf("You lose! The secret number is %d", secret_number);
}
}
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)How it works.
First, define the maximum of guesses:
const int MAX_GUESS = 4;Code language: C++ (cpp)Second, generate a random number between 0 and 10:
// Get a random number between 0 and 10
srand(time(NULL)); // call once only
secret_number = rand() % 10 + 1;Code language: C++ (cpp)Third, allow users to prompt a number until the number of guesses reaches MAX_GUESS or the number equals the secret_number:
while (number != secret_number && guess < MAX_GUESS)Code language: C++ (cpp)Fourth, increase the guess and prompt for an input:
// increase the guess
guess++;
// prompt for an input
printf("\nPlease enter a number (0 - 10):");
scanf("%d", &number);Code language: C++ (cpp)Fifth, display a success message if the input number matches the secret number:
if (number == secret_number)
{
printf("Bingo! you got it.\n");
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Sixth, show a message to the users if the number is lower or higher:
if (number > secret_number)
printf("No, it is smaller.\n");
else
printf("No, it is bigger.\n");Code language: C++ (cpp)Seventh, display the remaining guesses or a failed message if the guesses have been used:
// show the remaining guesses
if (MAX_GUESS - guess > 0)
printf("%d guess(es) left\n", MAX_GUESS - guess);
else
printf("You lose! The secret number is %d", secret_number);Code language: C++ (cpp)Summary #
- Use the C while loop statement to repeatedly execute a code based on a condition checked at the beginning of each iteration.