Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the C if...else statement to execute one or more statements conditionally.
Introduction to the C if…else statement #
An if statement can have an optional else clause like this:
if (expression)
{
// if statement
}
else
{
// else statement
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)If the expression evaluates to true (or a non-zero value), the statement in the if block will execute. However, if the expression evaluates to false (or zero), the statement in the else clause will execute instead.
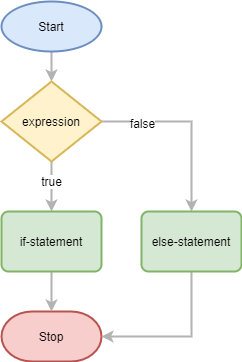
The following flowchart illustrates how the if…else statement works:
C if…else example #
The following example uses the if...else statement to display a message to the output:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 14;
if (age > 16)
{
printf("You can drive.\n");
}
else
{
printf("You are not old enough to drive.\n");
}
return 0;
}Code language: PHP (php)Since the age is 14, which is greater than 16, the statement in the else block executes and shows the following message:
You are not old enough to drive.More C if…else statement example #
The following program uses the if...else statement to check if an input number is an odd or even number:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
// prompt for an integer
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
// show the result
if (number % 2 == 0)
{
printf("%d is an even number.", number);
}
else
{
printf("%d is ann odd number.", number);
}
return 0;
}Code language: PHP (php)If you enter 10, the expression 10 % 2 == 0 returns 5 which is true. Therefore, the program will show the following message:
Enter an integer: 10
10 is an even number.However, if you enter 5, the expression 5 % 2 == 0 returns false. The statement in the else clause will execute and show the following message:
Enter an integer: 5
5 is ann odd number.Summary #
- Use the C
if...elsestatement to execute a code block when a condition is true or another code block when the condition is false.