Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about C for loop statement to execute a block of code repeatedly.
Introduction to C for loop statement #
Sometimes, you want to repeatedly execute a code block a number of times. To do it, you can use the for loop statement.
Note that if you want to execute a code block based on a condition, you can use the while or do…while statement.
The following shows the syntax of the for loop statement:
for (initialization; condition; update)
{
// statements
}Code language: C++ (cpp)The for loop statement has three expressions separated by a semicolon (;): initialization, condition, and update .
initialization
The for statement executes the initialization expression only once when the loop first starts. Typically, you initialize a variable in the initialization expression.
condition
The for statement evaluates the condition expression at the beginning of each iteration. If the result is non-zero (or true), the for statement executes the statements within its body surrounded by the curly braces {}. However, if the result is zero (or false), the for statement ends.
update
The for statement evaluates the update expression at the end of each iteration. Typically, you increase/decrease the loop counter in the update expression.
In the for statement, all three expressions are optional. However, the semicolon must remain. If you skip all the expressions, the for statement will look like this:
for(;;)
{
}Code language: CSS (css)In this case, you’ll have an indefinite loop. And you need to use the break or return statement to break out of the loop.
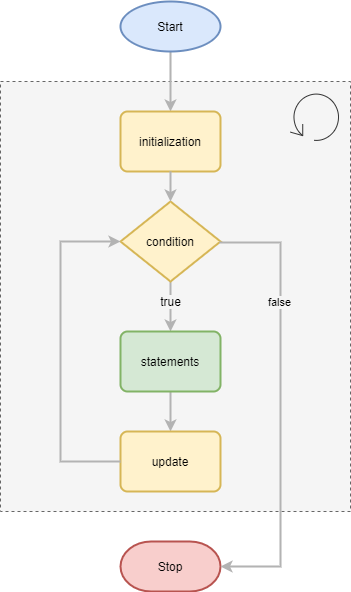
The following flowchart illustrates how the C for loop statement works:
C for loop statement examples #
Let’s take some examples of using the for loop statement.
1) A simple for loop statement example #
The following example uses a for loop to display numbers from 0 to 4:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
const int MAX = 5;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", i);
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Output:
0 1 2 3 4How it works.
Step 1. The for statement assigns 0 to i when the loop starts:
i = 0And the for statement only assigns 0 to i once.
Step 2. The for statement checks if i is less than MAX, which is 5. In the first iteration, since i is zero, the for statement executes the statement inside its body to output the value of i to the screen.
printf("%d ", i);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 3. The for statement executes the third expression at the end of the iteration that adds one to i:
i++Starting from the second iteration, the for statement repeats steps 2 and 3 until the expression i < MAX becomes false (zero).
Since the MAX is 5, the for statement executes the statement inside its body precisely 5 times. As a result, you’ll see 5 numbers from 0 to 4 in the output.
2) Using for loop to display even numbers #
The following example uses a for statement to display even numbers between 0 and 10:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
const int MAX = 10;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
return 0;
}Code language: PHP (php)Output:
0 2 4 6 8 How it works.
In this example, the for statement executes its body 10 times. The program checks if the current number is even in each iteration and displays it.
To check if a number is even, you compare the remainder of the division of a number and 2. If the result is zero, the number is even.
3) Using for loop statement to calculate the sum of consecutive numbers #
The following example uses a for loop statement to calculate the sum of consecutive numbers from 1 to n, where n is an input number:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// prompt for a number
int n;
printf("Enter the a positive number:");
scanf("%d", &n);
/// calculate the sum
int i, total = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
total += i;
// show the output
printf("The sum of numbers from 1 to %d is %d\n", n, total);
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)How it works.
In this example, the for executes its body n times where n is the input number. In each iteration, it adds the value of the current number to the total.
Note that if you apply a formula in Math, you don’t need a loop to calculate the sum of consecutive numbers from 1 to n. For example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// prompt for a number
int n;
printf("Enter the a positive number:");
scanf("%d", &n);
/// calculate the sum
int total = n * (n + 1) / 2;
// show the output
printf("The sum of numbers from 1 to %d is %d\n", n, total);
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Summary #
- Use the C
forloop statement to execute a code block repeatedly.