Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about various C float types, including float, double, and long double.
Introduction to C float types #
Floating-point numbers are numbers that have a decimal point. For example, 3.14 is a floating-point number. C has two floating-point types:
- float: single-precision floating-point numbers
- double: double-precision floating-point numbers.
The following example uses the float and double keyword to define floating-point number variables:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( )
{
float x = 0.1,
y = 0.1,
z = 0.1;
float total = x + y + z;
printf("The sum is %.20f\n", total);
return 0;
}
Code language: C++ (cpp)Output:
The sum is 0.30000001192092896000Code language: C++ (cpp)How it works.
- First, define three floating-point numbers x, y, and z.
- Second, add three numbers up and display the result.
The sum of 0.1, 0.1, and 0.1 is not 0.3 but 0.30000001192092896000. This is due to the precision of the floating-point numbers.
What is precision? #
If you consider the fraction 5/3, this number can be represented in decimal as 1.666666666... with infinite 6.
Since computers use a fixed number of bits, they cannot store an infinite number. Instead, computers store these numbers with precision.
The precision is expressed as a number of significant digits. In other words, precision is defined as how many digits a number can represent without data loss.
For example, the float type with 4 bytes = 4 x 8 bits = 32 bits, is for numbers with single precision. It means that a float gives 1 sign bit, 8 bits of exponent, and 23 bits of significand.
The double type is for a number with the double-precision that gives 1 sign bit, 11 bits of exponent, and 52 bits of significand. (8 bytes x 8 bits = 64 bits = 1 bits + 52 bits + 11 bits).
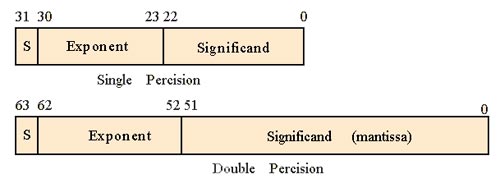
Short and long qualifiers #
Like integers, you can apply the short and long qualifiers to control the size of the floating-point type. The following table shows the floating-point types in C.
| Type | Size | Ranges | Smallest Positive Value | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| float | 4 bytes | ±3.4E+38 | 1.2E-38 | 6 digits |
| double | 8 bytes | ±1.7E+308 | 2.3E-308 | 15 digits |
| long double | 10 bytes | ±1.1E+4932 | 3.4E-4932 | 19 digits |
It is important to note that this is only the minimal requirement for storage size defined by C.
Float ranges and precision #
To find the value ranges of the floating-point number, you can use the float.h header file. This header file defines macros such as FLT_MIN , FLT_MAX and FLT_DIG that store the float value ranges and precision of the float types.
The float.h also defines macros for double and long double with the prefixes DBL_ and LDBL_.
The following program illustrates your system’s storage size and precision of floating-point numbers.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <float.h>
int main( )
{
printf("Storage size: %d bytes\n"
"Minimum float value: %E\n"
"Maximum float value: %E\n"
"Precision: %d decimal digits\n",
sizeof(float),
FLT_MIN,
FLT_MAX,
FLT_DIG);
puts("\nExample of float precision:\n");
double d = 12345.6;
float f = (float)d;
printf("The floating-point number d 18.10f\n", d);
printf("Stored in a variable f of type float as the value %18.10f\n", f);
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Summary #
- Floating-point numbers are numbers that have a decimal point.
- Use the
floatto declare the float variables.